
Ready To Place Your
Next Trade?
Choose a market, set your order, and manage risk in one place.


Ethereum is more than just a cryptocurrency. At the core of its power lies the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), the global decentralized computer that makes smart contracts and decentralized applications (DApps) possible. As the engine of Ethereum’s decentralized blockchain, the EVM is central to its secure, peer-to-peer architecture that operates without a central authority. Without the EVM, Ethereum would not have become the leading platform for innovation in blockchain technology. The EVM represents one of Ethereum’s innovations that has influenced the broader blockchain ecosystem.
This article explains what the Ethereum Virtual Machine is, how it works, why it matters, and how it transformed blockchain into a programmable ecosystem.
[ez-toc]

The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the decentralized software environment that executes smart contracts on Ethereum. It acts as a global computer where developers can deploy applications that run exactly as programmed without downtime or interference.
In simple terms:
A smart contract is a self-executing program that runs on the EVM, automatically enforcing and executing agreement terms when predefined conditions are met. This enhances transparency, security, and reduces the need for intermediaries.
The EVM ensures that every transaction, from sending ETH to interacting with a DeFi protocol, is validated in the same way across the entire Ethereum network.
In crypto, the EVM is crucial because it provides a shared, trustless environment for running applications. Unlike traditional apps, which rely on centralized servers, DApps powered by the EVM run on thousands of independent Ethereum nodes worldwide. Ethereum operates as a public blockchain, allowing anyone to participate in the network.
This makes Ethereum applications:
The EVM is what allows Ethereum to go beyond payments and power an entire Web3 ecosystem.
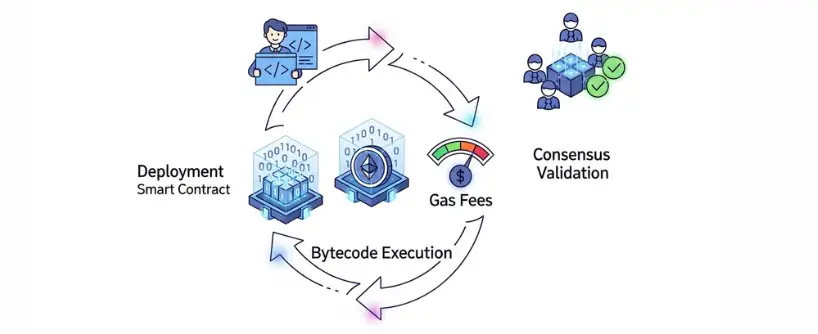
The EVM is like a sandboxed computer inside every Ethereum node. Here is how it works step by step:
This process ensures that all nodes validate transactions in the same way, maintaining security and decentralization.
The result is a decentralized computer that runs reliably and consistently, no matter how complex the smart contract.

To understand Ethereum, it helps to view it as two main components:
Together, they allow Ethereum to function as both a payment system and a programmable blockchain for applications.
This dual nature is why Ethereum supports thousands of DApps while Bitcoin remains focused on value transfer.
The EVM allows Ethereum to:
Without the EVM, Ethereum would simply be a cryptocurrency like Bitcoin, rather than a foundation for Web3.
The EVM’s importance comes from enabling thousands of developers to build on a shared infrastructure.
Advantages include:
This explains why most blockchain projects today are EVM-compatible, meaning they copy or extend Ethereum’s virtual machine to benefit from its developer ecosystem. Ongoing development and protocol upgrades have contributed to the EVM’s widespread adoption.
Some well-known DApps powered by the Ethereum Virtual Machine include applications built on the ethereum platform, which process ethereum transactions involving various digital assets:
Each of these relies on the EVM to ensure transactions and contracts execute fairly across the network.
What is EVM?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is the decentralized computing environment that runs smart contracts and DApps on Ethereum. It is a core component of the ethereum protocol, responsible for executing smart contracts using ether, the network’s native token.
What is EVM in crypto?
In crypto, the EVM is the system that ensures decentralized apps can run without centralized control, making Ethereum programmable and trustless. Ethereum is the second largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, and ether is used to pay transaction fees for executing smart contracts and transactions on the network.
What does EVM do in Ethereum?
The EVM executes smart contract code, validates results, and ensures every node in the network produces the same outcome. It processes data and validates transactions, allowing users to interact with the system through ethereum wallets, which securely manage private keys and authorize transactions.
Why is the Ethereum Virtual Machine important?
The EVM enables developers to build thousands of decentralized applications, from finance to gaming, on a shared infrastructure. It supports a wide range of digital currencies and digital assets, and enables new business models by allowing parties to interact without intermediaries.
Is the EVM unique to Ethereum?
Ethereum pioneered the EVM, but many blockchains such as Polygon, Avalanche, and BNB Chain use EVM-compatible systems so they can run the same apps. The EVM was proposed as part of Ethereum’s original blockchain, and protocol upgrades—including the transition from proof of work to proof of stake—have improved energy usage and security.
What is the role of the Ethereum Foundation, hard forks, and consensus?
The Ethereum Foundation is responsible for the formal development and support of Ethereum, funding projects and managing protocol upgrades. Hard forks, such as the one that created Ethereum Classic, are significant changes to the network that may result from security events or community decisions. Consensus among other validators is essential for maintaining the integrity of the blockchain, especially in the proof of stake system.
How are ether holdings and proof of stake involved in Ethereum?
In Ethereum’s proof of stake system, users with ether holdings can participate as validators to propose and attest to new blocks, minting new ETH. This process involves multiple parties and other validators, ensuring network security and decentralization.
What is the legal status of ether and Ethereum’s native token?
Ether, Ethereum’s native token, is generally classified as a commodity rather than securities. Its legal status as intangible personal property or a controllable electronic record (CER) varies by jurisdiction, but it is distinct from traditional securities.
How does the EVM eliminate the need for a central authority?
The EVM enables decentralized business processes by allowing smart contracts to execute automatically without relying on a central authority. This ensures trustless interactions between parties and supports new forms of business and governance.
How do the EVM and Ethereum work together to support decentralized applications and digital assets?
The EVM and Ethereum work together to provide a secure, decentralized platform for building and running decentralized applications and managing digital assets, supporting a broad ecosystem of digital currencies and innovative business models.
The Ethereum Virtual Machine is the heart of Ethereum’s innovation. By creating a global decentralized computer, Ethereum allowed developers to build financial systems, NFT marketplaces, and governance tools directly on-chain.
Today, the EVM is more than just Ethereum’s engine, it has become the standard for blockchain programmability. Understanding what the EVM is, how it works, and why it matters is essential for anyone exploring Web3.
Disclaimer: Trading digital assets involves risk and may result in the loss of capital. Always do your own research. Terms, conditions, and regional restrictions may apply.
