


When you open a trading platform like Bitunix, one of the first things you face is the decision of which order type to use. Should you press the “Market” button to buy instantly, set a “Limit” order to wait for your price, or protect yourself with a “Stop Loss”? These terms can sound intimidating, but they are simply tools that give you more control over your trades. Understanding how they work is essential if you want to trade with confidence in the fast-moving world of cryptocurrency.
This guide breaks down the main order types available on Bitunix. It explains how market, limit, stop, and stop limit orders work in real trading situations, why they matter, and how advanced options like OCO and trailing stop can help you manage trades more effectively. By the end, you will understand how to choose the right order type for different situations.
[ez-toc]

A market order is the simplest type of order. It tells the exchange to buy or sell immediately at the best available price, ensuring immediate execution of your trade. Think of it like walking into a store and agreeing to pay the listed price right away.
Market orders focus on speed rather than price precision. They are useful when you want to enter or exit quickly, especially on high-liquidity pairs like BTC/USDT where spreads are narrow. Market orders are executed as long as there are willing buyers or sellers in the market.
Example: If Bitcoin is trading around 40,000 USDT and you place a 1,000 USDT market buy, your order will be filled instantly. However, depending on the liquidity, your average fill price could be slightly higher, such as 40,010 or 40,050.
Best use cases:
The downside is slippage. If the market is volatile or liquidity is thin, you may get a worse price than expected. Always check the order book depth if you are trading larger amounts.
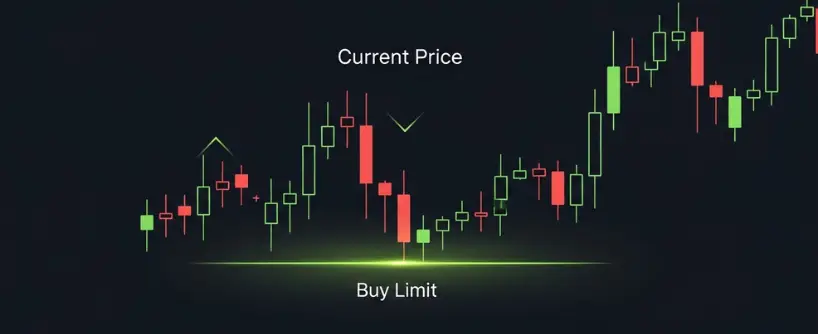
A limit order allows you to set the exact price at which you want to buy or sell. For buy limit orders, you can set the maximum price you are willing to pay, and for sell limit orders, you can set the minimum price you are willing to accept. A sell limit order is an instruction to sell at a specified minimum price or higher. Your order will only execute if the market reaches that price or better. This gives you control over the price, but there is no guarantee that it will fill.
Example: If Bitcoin is trading at 40,000 USDT but you only want to buy if it dips to 39,500, you can place a buy limit order at 39,500. The order will sit on the order book until the market reaches that price. If it never does, your order will remain unfilled.
Advantages:
Disadvantages:

Traders often ask whether a market order or limit order is better. The answer depends on your situation.
Rule of thumb: If you need to exit immediately to protect your account, use a market order. If you are planning an entry at a specific price level, use a limit order.
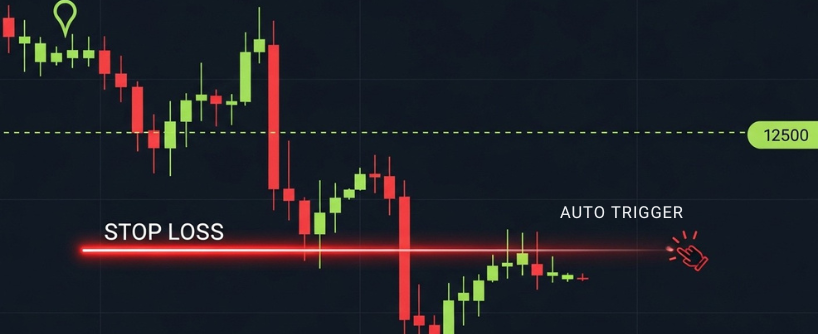
A stop loss order protects you by automatically selling when the market moves against you. Stop loss orders are a key risk management tool designed to limit losses by setting a specified price at which the order is triggered. It helps you limit potential losses without needing to constantly watch the chart.
Example: You buy Bitcoin at 40,000 USDT and place a stop market order at 38,500. If the price falls to 38,500, your stop is triggered, and the system executes a market sell order to close your position. Once the stop price is reached, the order becomes a market order, and the execution price may differ from the trigger price, especially in fast-moving or volatile markets. This prevents further losses if the market keeps dropping.
Types of stop orders:
Stop loss orders automatically sell a security at the prevailing market price once the specified price is reached, helping to protect against downside risk when a stock falls. The current market price and market price at the time of execution can impact the final execution price, especially during periods of high volatility.
A stop loss is not optional in serious trading. It enforces discipline and is an essential part of risk management strategies to limit losses and manage downside risk.
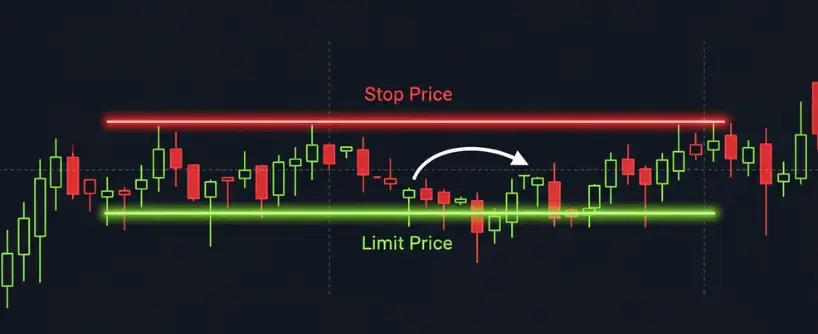
A stop limit order combines the ideas of a stop and a limit. You set a trigger price and a limit price. The specified limit price is the minimum price at which you are willing to sell after the stop price is triggered. When the stop price is reached, a limit order is placed at the price you define.
Example: You buy Bitcoin at 40,000 and want to protect your position if it falls, but you do not want to sell below your desired price. You set a stop at 38,500 (the set price at which the order is triggered) and a limit at 38,400 (the specified limit price, which is also your price limit and lowest price you are willing to accept). If the stock price drops to 38,500, your stop limit order is triggered and a limit order is placed at 38,400. This price limit helps ensure you do not sell below your minimum price, even if the stock price falls rapidly. If the market falls too fast and skips your limit, the order may not fill.
Best use cases:
Bitunix offers more than just the basic order types. Advanced tools help traders manage risk and strategy more effectively:
Some advanced order types, such as ‘All or None,’ ensure the entire order is filled or not at all, which can be important when you want to sell securities without partial fills.
These tools are particularly helpful for traders who cannot monitor the market all day.
Bitunix makes these tools simple to use, combining a clean interface with the flexibility needed by more advanced traders.
What is a market order?
It is a stock order that executes immediately at the best available price. Best for speed, not price precision.
What is a limit order?
It is a stock order that executes only at your chosen price or better. Best for control, not speed.
Market vs limit order: which is safer?
Neither is inherently safer. Market orders guarantee execution but may slip in volatile conditions, causing execution prices to vary. Limit orders ensure price precision but may not fill. Understanding execution prices is important for managing risk, especially during market swings.
What is a stop loss order?
A stop loss is an order to sell when the price reaches a certain level. It automatically closes your trade when the market moves against you, using sell orders strategically to manage risk. Stop loss orders can help protect against market swings by automatically selling when prices move sharply.
What is a stop limit order?
It is a hybrid order that places a limit order once a stop price is reached. It offers price control but may not fill in fast markets. Stop limit orders are commonly used in stock trading to manage risk and control execution prices.
When should I use a trailing stop?
Trailing stops are useful when you want to let profits run while locking in gains if the market reverses.
What is an OCO order?
An OCO order links two orders together. For example, you can set a stop loss and a take profit at the same time. Once one executes, the other cancels automatically.
Do these order types work the same on all exchanges?
No. Each exchange implements order types slightly differently. Managing risk involves understanding how different order types work and how they can be used to protect investments. Always review how Bitunix or any other platform defines the rules before using them.
What are stock orders?
Stock orders refer to the various instructions traders use to buy or sell stocks, such as market, limit, stop-loss, and stop-limit orders.
What is a fair price?
A fair price is the price at which a security can be quickly sold and converted to cash, reflecting its marketability.
How do I use trading strategies with different order types?
Choosing the right order type is an important part of a trading strategy to manage risk and optimize trade outcomes.
What is stock trading?
Stock trading involves buying and selling shares using various order types to manage risk and take advantage of market opportunities.
Can I use these order types for mutual funds?
Mutual funds are typically bought or sold through broker-dealers, and the process may differ from stock trading. Broker-dealers execute buy or sell orders for mutual funds and may earn commissions for these transactions.
Order types are the control panel for your trading. Market orders give you speed. Limit orders give you control. Stop losses give you protection. Stop limit orders give you precision. Advanced tools like OCO and trailing stops add flexibility for different market conditions.
On Bitunix, all these tools are available in one clean interface. Start small, test each type in real scenarios, and gradually build your confidence. With practice, you will learn how to combine order types to fit your personal trading style and risk tolerance.
Disclaimer: Trading digital assets involves risk and may result in the loss of capital. Always do your own research. Terms, conditions, and regional restrictions may apply.
