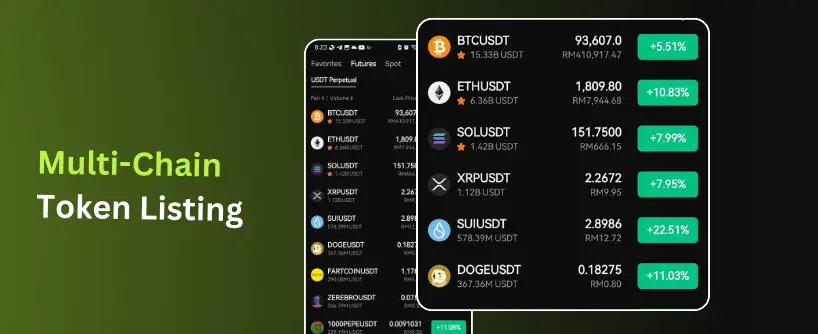
Anyone deep in crypto has heard phrases like “this protocol runs on that blockchain,” but the blockchain vs protocol difference isn’t always clear.
While the terms are often tossed around interchangeably, they refer to two very different layers of the Web3 ecosystem. Understanding the distinction isn’t just helpful — it’s essential. Especially in 2025, where traders interact with multiple chains, bridges, and platforms daily, clarity matters more than ever.
Let’s break it down, using Bitunix as the lens through which to understand both.
[ez-toc]
Why People Confuse Blockchain with Protocol
It’s easy to blur the line. After all, both concepts sit at the core of how cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications work. But here’s the simplest way to frame it:
They work together, but they are not the same. Think of it as hardware vs. software logic.
The Blockchain: Your Digital Highway
A blockchain is a distributed ledger maintained by a network of nodes. It records transactions in chronological order and secures them through cryptography.
What makes a blockchain trustworthy is that once data is written, it’s locked in. No central authority can tamper with it, and everyone can verify it.
Key Traits:
-
Decentralized — run by independent nodes
-
Immutable — historical data cannot be changed
-
Transparent — full transaction records available to all
Examples You Know:
-
Bitcoin — Peer-to-peer digital cash secured via proof-of-work
-
-
Solana, Avalanche, BNB Chain — Built for performance and DeFi use cases
These are the highways where crypto activity travels.
Protocols: The Invisible Logic Behind Every Blockchain
If blockchains are the highways, then protocols are the traffic laws — the invisible but critical rules everyone must follow.
In crypto, a protocol is a set of rules that defines how the blockchain operates:
-
How blocks are produced
-
How transactions are validated
-
How consensus is reached
-
How rewards are distributed
-
How participants communicate across the network
You don’t always see the protocol at work — but it determines every action on-chain.
Common Types:
-
-
Layer 2 Scaling Protocols: Arbitrum, Optimism
-
Interoperability Protocols: Cosmos IBC, Polkadot XCMP
-
DeFi Protocols: Uniswap, Aave, Curve
Each of these serves a purpose — and may operate on top of or within different blockchains.
Blockchain vs Protocol: Side by Side
Here’s where the line gets clearer:
|
Blockchain |
Protocol |
| What It Is |
Ledger system to store transactions |
Rule system that defines how blockchain works |
| Exists As |
Data structure |
Code + logic layer |
| Can You See It? |
Yes, it’s the interface and history |
Not directly — it’s the behavior behind the scenes |
| Examples |
Ethereum, Solana, BNB Chain |
ERC-20, PoS, Uniswap v3, IBC |
| User Role |
You interact by sending/receiving tokens |
You depend on it when using the blockchain |
Understanding this distinction is critical for anyone trading, investing, or building in crypto space.
Examples That Make It Clear
Here are three practical examples that illustrate how protocols define blockchain behavior:
Ethereum Protocol
-
Sets how validators stake ETH to secure the network
-
Defines smart contract structure and interaction
-
Establishes gas fee models and execution rules
Bitcoin Protocol
Uniswap Protocol
Each example shows how protocol rules shape user experience without the user needing to directly interact with the protocol itself.
Why It Matters for Traders in 2025
With crypto growing more complex, knowing how protocols and blockchains relate gives traders a sharper edge. Here’s why:
- Cross-Chain Trading Is the Norm – Apps like Curve and Aave now operate on multiple blockchains. Understanding the protocol layer helps you avoid confusion and route your trades properly.
- Security Depends on Protocol Design – A poorly audited protocol can put your funds at risk, no matter how secure the blockchain it’s running on.
- Token Value Comes from Protocol Strength – When you invest in tokens like AVAX or DOT, you’re also betting on the future of their protocol layer — not just their network.
- Protocol Upgrades Can Shift Entire Markets – Ethereum’s Dencun upgrade in 2025 reduced L2 fees dramatically, making rollups more attractive. Traders who understood the protocol impact positioned themselves early.
How Bitunix Handles Blockchain + Protocol Interactions
Bitunix streamlines protocol complexity so traders don’t have to think about it — but it’s still happening behind the scenes. Here’s how:
- Cross-Chain Listings – You can trade tokens built on Ethereum, Solana, BNB Chain, and Layer 2s like Optimism — without switching platforms.
- Wallet Routing Logic – Depositing ERC-20 vs BEP-20 tokens? Bitunix automatically adjusts routing based on protocol type.
- Smart Contract Connectivity – Products like Bitunix Earn integrate with DeFi protocols to generate yield — seamlessly connected behind the scenes.
- Risk Management Adjustments – Different protocols come with different volatility and margin profiles. Bitunix adapts risk engines accordingly.
- The result is a smooth trading experience — but one that’s protocol-aware at its core.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Is every blockchain powered by a protocol? Yes. A blockchain without a protocol would be non-functional — the protocol defines its rules.
- Can a protocol exist without its own blockchain? Yes. For example, Uniswap is a protocol that runs on Ethereum — it doesn’t require its own chain.
- Is Ethereum a blockchain or a protocol? Both. Ethereum is a blockchain, but the rules that make it work are governed by the Ethereum protocol.
- What’s the difference between Layer 1 and Layer 2 protocols? Layer 1 is the base chain (e.g., Ethereum, Solana). Layer 2 is built on top (e.g., Optimism, Arbitrum) to improve speed or reduce cost.
- Why does this distinction matter on Bitunix? Because trading fees, asset behavior, and compatibility are often dictated by the protocol layer — not just the blockchain label.
What This Means for Your Strategy
You don’t need to be a developer to understand the blockchain vs protocol difference. But if you’re trading, staking, or investing — especially on a platform like Bitunix — this clarity helps you:
-
Make informed token choices
-
Understand risk beyond the chart
-
Anticipate how upgrades affect price action
-
Use Bitunix tools with confidence
Bitunix handles the technical layers — but when you understand what’s under the hood, you trade smarter.
Explore cross-chain tokens, protocol-integrated features, and advanced derivatives — all on Bitunix.