
Have you ever tried to sell something truly unique – a rare collectible, a piece of heirloom furniture – only to find there’s no one around to buy it? That frustrating feeling, the silence where a transaction should be, is what the crypto world calls illiquidity. For years, it was the ghost haunting the halls of decentralized finance (DeFi). How could we build a new financial system if you couldn’t reliably trade one digital asset for another?
Then, a revolution appeared from the code. The solution was a liquidity pool.
But what is a liquidity pool? In its simplest form, it’s a shared pool of crypto assets locked in a smart contract that enables decentralized exchanges to operate without traditional market makers. It is the beating heart of DeFi, the engine that powers efficient trading, and the reason you can swap tokens at any hour of the day. This isn’t just a technical feature; it’s a paradigm shift. And to understand the future of finance, you must understand why crypto needs them.
[ez-toc]
The Problem Before Pools

Before we dive into the solution, let’s truly appreciate the problem. Imagine the earliest decentralized exchanges (DEXs). They were like ghost towns. They had a marketplace, but no shopkeepers.
On centralized exchanges like Coinbase or Binance, traditional market makers, large firms with massive capital, are the shopkeepers. They constantly list buy and sell orders, creating a vibrant market. They provide liquidity, ensuring there’s always someone to facilitate trades with you. But this relies on traditional intermediaries, which is precisely what crypto set out to eliminate.
Early DEXs used on-chain order books, but low liquidity made trade execution slow and inefficient compared to centralized exchanges. If you wanted to sell a lesser-known altcoin, you had to hope and often wait for a buyer to appear who wanted that exact coin at your exact price. This led to low liquidity, massive price swings on small trades (slippage), and a clunky user experience. It was a system struggling to breathe. The question was clear: how do we create liquidity out of thin air?
The Invention of the Automated Shopkeeper: How Liquidity Pools Work
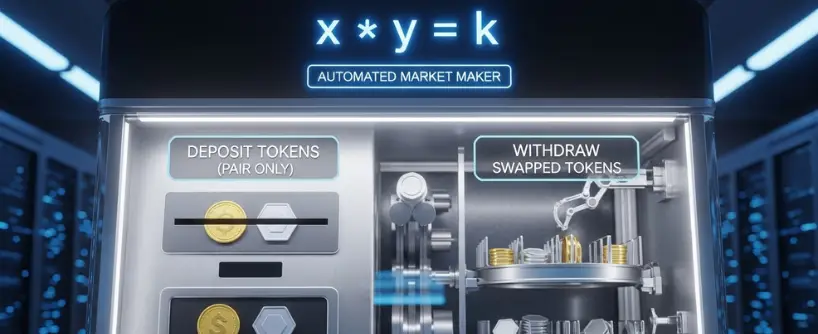
The answer was brilliantly simple. Instead of waiting for a matching buyer and seller to show up, why not create a reservoir of funds that anyone can trade against? Welcome to the liquidity pool.
Think of it as a communal vending machine. Instead of a company stocking it, the people do.
- Users Provide Liquidity: People, known as liquidity providers (LPs), lock up pairs of tokens into a smart contract. For example, to provide liquidity for an ETH/USDT pair, you must deposit an equal value of both ETH and USDT.
- The Pool is Created: This combined capital forms the liquidity pool. This pool is now the counterparty for every trade.
- Automated Market Makers (AMMs) Determine Prices: This is the magic. The pool uses an automated market maker (AMM) algorithm, a formula that automatically determines the exchange rate between the two tokens based on their ratio within the pool. The most common formula (x*y = k) ensures that the larger a trade is relative to the pool, the more the price shifts, mimicking supply and demand.
- Trading Happens Instantly: When you want to swap ETH for USDT, you don’t need a counterparty. You trade directly with the pool. The AMM calculates the price, you get your USDT, and the pool’s ratio changes slightly, adjusting the price for the next trader.
This genius mechanism provides continuous liquidity, 24/7. The vending machine is always stocked, always open.
The Incentive: How Liquidity Providers Earn Fees

Why would anyone lock up their precious crypto in a pool? The incentive is yield generation.
Every time a trader uses the pool to make a token swap, they pay a small transaction fee (typically 0.1-0.3%). This fee is then distributed proportionally to all the liquidity providers in that pool. Your share of the fees corresponds directly to your share of the total pool.
It’s a form of earning passive income. Your assets are put to work to facilitate transactions, and you earn a slice of all the trading fees generated by the pool’s activity. This process of depositing funds to earn rewards is also often called liquidity mining or yield farming, especially when protocols distribute governance tokens as an extra incentive.
To track your share of the pool, you receive liquidity pool tokens (LP tokens). These LP tokens represent your claim to your portion of the underlying assets plus your accrued fees. When you want to exit, you simply return your LP tokens to the contract to reclaim your initial deposit plus your earnings.
Beyond Swaps: The Deeper Impact of Crypto Liquidity Pools

The innovation of crypto liquidity pools extends far beyond simple swaps. Their ability to determine asset prices algorithmically has unlocked a universe of new possibilities:
- Price Discovery: In illiquid markets for new tokens, AMMs provide a transparent and algorithmic method for price discovery, allowing the market to determine prices organically.
- Accessible Financial Services: Liquidity pools aim to democratize finance. Anyone in the world with an internet connection and some crypto can become a market maker and earn passive income, a role previously reserved for giant institutions.
- Composability: These pools are Lego blocks for DeFi. They are used for lending, borrowing, derivatives, and much more, all because they provide a reliable, on-chain source of decentralized liquidity.
This makes liquidity pools far more than a tool, they’re a gateway to accessible financial services for millions.
The Associated Risks

No financial innovation is without its perils. While liquidity pools offer numerous benefits, crypto liquidity providers must be aware of the associated risks.
- Impermanent Loss: This is the big one. It happens when the value of your deposited assets shifts notably from their original price at the time of deposit. You could end up with less dollar value than if you’d simply held the assets, even after accounting for accrued fees. It’s not a loss in the traditional sense but an opportunity cost.
- Smart Contract Vulnerabilities: Pools are powered by code. If there’s a bug or exploit in the smart contracts, funds can be stolen. It’s crucial to use well-audited protocols with strong security measures.
- Counterparty Risk: In some advanced pools that concentrate liquidity within specific price ranges, the risk profile can be more complex.
Understanding these risks is not a reason to avoid participation, but a necessary step for informed involvement.
Liquidity Pools vs Traditional Market Makers

In traditional markets, market makers manually balance buyers and sellers, often through banks or brokers. In contrast, crypto liquidity pools work automatically, without intermediaries.
- Traditional market makers: Require human intervention, centralized control, and often charge higher fees.
- Liquidity pools: Use smart contracts, ensure decentralized liquidity, and lower costs.
This shift has redefined trading from relying on Wall Street intermediaries to enabling global, decentralized trading at the click of a button.
Conclusion
So, what is a liquidity pool? It’s not just a bucket of tokens – it’s the engine of decentralized finance. From facilitating trades and powering decentralised exchanges to offering yield farming opportunities and democratizing access to financial tools, liquidity pools represent a revolution.
Of course, there are associated risks, but with proper research and security measures, they open doors to accessible financial services for anyone with an internet connection.
In essence, liquidity pools aim to do what traditional intermediaries never could: create a borderless, efficient, and rewarding financial ecosystem.
And that’s why the answer to why crypto needs them is simple: because without them, the entire DeFi landscape would grind to a halt. Liquidity pools power the DeFi economy, reward providers with passive income, and ensure markets remain liquid, fair, and efficient.
FAQs
How do automated market makers work in liquidity pools?
Automated market makers (AMMs) use algorithms instead of order books to set prices in crypto trading, making swaps faster and ensuring fair price discovery.
How do crypto liquidity pools work?
Crypto liquidity pools work by allowing users to deposit assets into a smart contract, which creates a pool that traders can swap tokens against without needing direct buyers or sellers.
What are liquidity pool tokens (LP tokens)?
Liquidity pool tokens represent a user’s share of the pool. Holders can redeem them to withdraw their assets plus any trading fees earned.
What is liquidity mining?
Liquidity mining is when users deposit assets into pools and receive extra rewards, often in governance tokens, in addition to regular trading fees.
Why are liquidity pools important in decentralized finance?
In decentralized finance (DeFi), liquidity pools provide the foundation for trading, lending, and yield farming, making financial services more open and accessible.
How do liquidity pools strengthen the DeFi ecosystem?
They fuel the DeFi ecosystem by ensuring more liquidity, enabling token swaps, supporting yield farming, and promoting decentralized trading without intermediaries.
What does liquidity provision mean?
Liquidity provision is the act of supplying assets to a pool, which allows traders to swap tokens smoothly while providers earn passive income from trading fees.
Disclaimer: Trading digital assets involves risk and may result in the loss of capital. Always do your own research. Terms, conditions, and regional restrictions may apply.

