
When Ethereum launched in 2015, it followed Bitcoin’s model of Proof of Work (PoW) to secure its blockchain. However, Ethereum was always envisioned as more than a digital currency. It was designed to be a decentralized computing platform that could support smart contracts, decentralized applications, and financial ecosystems. To achieve that long-term vision, Ethereum needed a more sustainable and scalable consensus mechanism.
In September 2022, Ethereum made history by transitioning from Proof of Work to Proof of Stake (PoS), an event known as The Merge. This shift not only transformed Ethereum but also reshaped the entire blockchain industry. Today, in 2025, Ethereum’s Proof of Stake model continues to influence innovation across crypto, from staking to sustainability.
[ez-toc]
What is Proof of Stake?

Proof of Stake (PoS) is a consensus mechanism where validators secure the blockchain by staking their cryptocurrency as collateral. Instead of miners competing with computing power, validators are chosen to propose and confirm blocks based on the amount of ETH they stake and random selection.
Key features of PoS:
- Energy efficiency: Requires far less electricity than Proof of Work.
- Accessibility: Anyone with ETH can participate by staking directly or through staking pools.
- Security: Validators who act dishonestly risk losing their staked ETH.
Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work
To understand Ethereum’s transition, it is important to compare Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work:
| Feature | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| Security | Secured by mining power | Secured by staked ETH |
| Energy Use | Very high (requires mining rigs) | 99%+ lower energy consumption |
| Participation | Requires expensive hardware | Requires ETH stake (no hardware) |
| Rewards | Block rewards + fees | Staking rewards + fees |
| Accessibility | Limited to miners with resources | Open to all ETH holders |
Ethereum’s move to PoS cut energy consumption by more than 99%, making it one of the most environmentally significant changes in blockchain history.
Why Did Ethereum Transition to Proof of Stake?

Ethereum developers pursued Proof of Stake for several reasons:
- Scalability: PoS provides a foundation for future upgrades like sharding, enabling Ethereum to process more transactions at lower cost.
- Sustainability: Ethereum PoW consumed as much electricity as a small country. PoS reduces the environmental impact dramatically.
- Security: In PoS, attackers would need to control a large portion of ETH, making attacks economically unfeasible.
- Accessibility: PoS opens the door for everyday users to earn rewards through crypto staking without expensive mining rigs.
How Does Ethereum Proof of Stake Work?
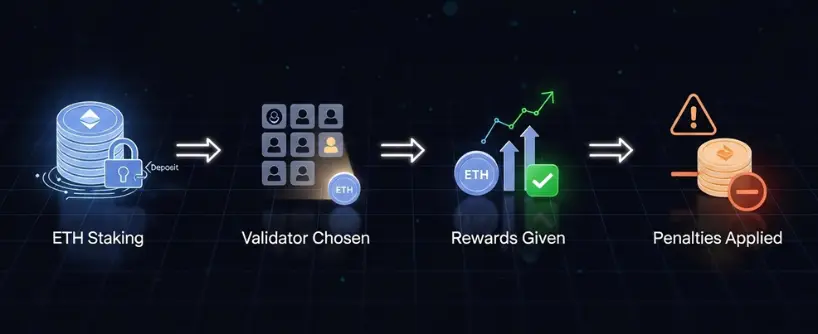
Ethereum PoS relies on validators instead of miners. Here’s how it works:
- Staking ETH: Users lock 32 ETH to become validators. Others can join staking pools with smaller amounts.
- Validator Selection: The network randomly selects validators to propose and validate blocks.
- Rewards: Validators earn rewards in ETH for honest participation.
- Penalties: Validators acting maliciously or going offline may lose part of their stake, a process called “slashing.”
This model makes Ethereum more decentralized, as staking pools and services allow millions of participants to contribute.
Crypto Staking on Ethereum

One of the biggest innovations after Ethereum’s transition is the rise of crypto staking. By staking ETH, users earn rewards similar to interest in traditional finance.
Benefits of staking ETH:
- Passive income through staking rewards.
- Contribution to Ethereum’s security and decentralization.
- Flexible options through centralized exchanges, DeFi platforms, and liquid staking protocols like Lido or Rocket Pool.
Risks of staking ETH:
- Lock-up periods depending on the staking method.
- Slashing risks if validators behave incorrectly.
- Market volatility affecting ETH value.
Ethereum Proof of Stake vs Ethereum Proof of Work

Before The Merge, Ethereum used Proof of Work. That model secured the blockchain but had limitations: high gas fees, energy usage, and scalability concerns.
After the transition, Ethereum’s Proof of Stake introduced:
- Lower energy costs (over 99% reduction).
- Foundation for scalability upgrades like danksharding and rollups.
- Improved accessibility with more participants joining staking.
In contrast, Ethereum Proof of Work continues only through forks like Ethereum Classic, but it no longer powers the main Ethereum blockchain.
Ethereum Blockchain After The Merge
Since 2022, the Ethereum blockchain has evolved significantly under PoS:
- DeFi growth: Staking has become a core part of decentralized finance.
- NFT stability: Lower environmental footprint helps Ethereum remain the leading NFT chain.
- Global adoption: Businesses and governments see PoS as more sustainable.
- Cross-chain activity: Ethereum’s PoS model integrates with bridges, rollups, and Layer 2 scaling.
In 2025, Ethereum remains the dominant platform for smart contracts and decentralized applications because of its PoS transition.
Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work: Industry Impacts
Ethereum’s move to PoS has influenced the broader blockchain world:
- Bitcoin Proof of Work remains unchanged, focusing on security through mining.
- Many new blockchains (Solana, Cardano, Polkadot) already use PoS, validating Ethereum’s shift.
- Regulators and institutions highlight Ethereum’s sustainability as a positive sign for crypto adoption.
This contrast between Bitcoin’s Proof of Work and Ethereum’s Proof of Stake shows how different models coexist, each serving different goals.
FAQs
What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism where validators secure the blockchain by staking cryptocurrency rather than using mining power.
What is Ethereum Proof of Stake?
Ethereum Proof of Stake is the current consensus model of Ethereum where validators stake ETH to secure the blockchain and earn rewards.
What is the difference between Proof of Stake and Proof of Work?
PoW relies on miners competing with computing power, while PoS relies on validators staking assets. PoS is more energy-efficient and accessible.
How does Ethereum Proof of Stake work?
Validators are randomly chosen to propose and verify blocks. They earn ETH rewards for honest work and risk slashing if they cheat.
What is crypto staking?
Crypto staking is the process of locking cryptocurrency in a Proof of Stake network to earn rewards and support security.
What happened to Ethereum Proof of Work?
Ethereum’s main chain no longer uses PoW. Some PoW forks like Ethereum Classic remain, but Ethereum itself runs entirely on PoS since 2022.
Conclusion
Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake was more than just a technical update. It redefined how blockchains can balance sustainability, scalability, and security. By cutting energy use, opening up staking to millions, and laying the groundwork for future upgrades, Ethereum changed blockchain forever.
As crypto evolves in 2025, Ethereum’s Proof of Stake model serves as a blueprint for innovation, proving that blockchains can adapt to global challenges while continuing to power decentralized finance, NFTs, and digital economies.


One reply on “How Ethereum’s Transition to Proof of Stake Changed Blockchain Forever”
This information is priceless. Where can I find out more?