Ethereum is often called the world’s first programmable blockchain. Unlike Bitcoin, which was designed mainly for payments and a store of value, Ethereum introduced the idea of smart contracts. A smart contract is a self executing program that runs on a decentralized blockchain, automatically enforcing the terms of an agreement without intermediaries. These digital agreements laid the foundation for decentralized applications, financial services, gaming ecosystems, and more, all built on the Ethereum platform—a decentralized platform that empowers developers to create and operate innovative solutions. Today, smart contracts are central to how modern blockchain systems operate. Ethereum’s innovations in programmable blockchain technology, such as scalability solutions and the pioneering of smart contracts, have positioned it as a leader in the blockchain industry.
[ez-toc]
What is a Smart Contract?

A smart contract is a self-executing digital agreement written in code, with the terms of the contract directly embedded into the software. Instead of relying on a third party to enforce the agreement, the blockchain itself ensures that once conditions are met, the contract executes automatically. The contract is executed without the need for the involved parties to trust each other, as the blockchain guarantees the outcome.
For example:
- A smart contract can release payment when a product is delivered.
- It can manage lending and borrowing without banks.
- It can power NFTs by linking ownership records to blockchain addresses.
- Smart contracts can securely store and process data, ensuring that transaction data and other relevant information are handled transparently.
In essence, a smart contract removes intermediaries, increases trust, and reduces costs. The source code of smart contracts is publicly available, allowing users to verify how agreements will be executed.
How Does Ethereum Work with Smart Contracts?
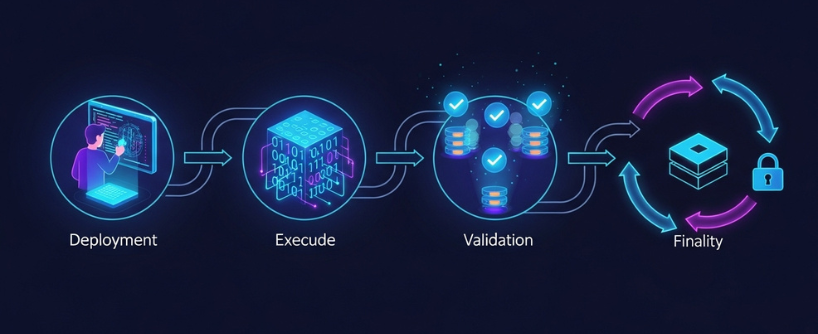
Ethereum works as a decentralized network that validates transactions and runs programs called smart contracts. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is responsible for executing smart contract code across the network. Here’s the process:
- Deployment: A developer writes code (usually in Solidity) and deploys it to the Ethereum blockchain.
- Execution: When users interact with the contract (e.g., buying tokens, joining a lending pool), the Ethereum network executes the code. The EVM manages the processes involved in running smart contracts.
- Validation: Network participants use a consensus mechanism to validate transactions. Other validators confirm the correctness of each block before it is added to the blockchain.
- Finality: Once confirmed, the action becomes irreversible on the blockchain.
The Ethereum protocol is regularly improved through protocol upgrades, which may change how validators propose and validate new blocks.
This innovation made Ethereum the first blockchain to move beyond simple transfers of cryptocurrency.
What Does Ethereum Do with Smart Contracts?

Ethereum enables much more than peer-to-peer payments. With smart contracts, developers can build:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Protocols like Uniswap and Aave allow trading, lending, and borrowing without banks.
- NFTs: Ethereum popularized non fungible tokens (NFTs), which are unique digital assets representing ownership of digital art, collectibles, virtual real estate, in-game assets, and more. These digital assets can be securely transferred on the blockchain, providing proof of authenticity and ownership.
- Gaming ecosystems: Smart contracts power in-game economies, ensuring transparent and fair ownership. Ownership of virtual real estate and in-game digital assets can be transferred securely between players, leveraging blockchain technology.
- DAOs (Decentralized Autonomous Organizations): Communities that govern themselves through coded rules.
Ethereum enables new business models by allowing anyone to create smart contracts and leverage smart contract functionality for decentralized finance, digital assets, and innovative applications.
In short, Ethereum transformed the blockchain from a digital currency ledger into a programmable economy.
What is Ethereum Used For Today?
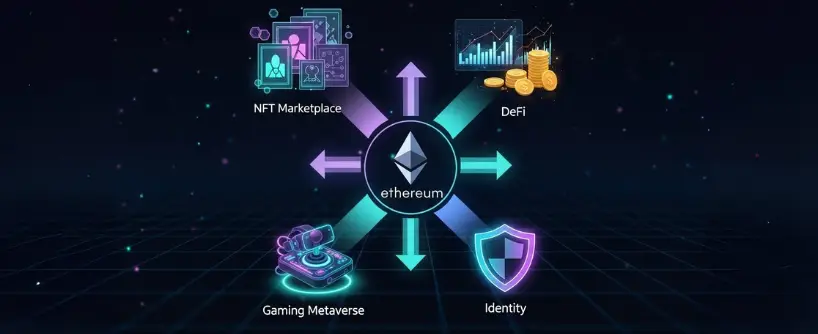
Ethereum is widely used across industries:
- Finance: Decentralized exchanges, stablecoins, and staking platforms. Ether (ETH), the native cryptocurrency of Ethereum, is used for paying transaction fees and powering decentralized applications.
- Art and Media: NFT art marketplaces like OpenSea.
- Gaming and Metaverse: Virtual lands and items tied to Ethereum are digital assets on a public blockchain network.
- Identity and Security: On-chain identity verification and decentralized storage. Ethereum wallets are essential for managing digital assets securely.
Ethereum is the second largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization and is widely used for digital currencies and other digital currencies.
With thousands of decentralized applications (DApps) built on its blockchain network, Ethereum is often called the backbone of Web3. The internet serves as the foundation for Web3, with Ethereum integrating seamlessly to support the next generation of decentralized applications.
Strengths and Limitations of Ethereum Smart Contracts

Strengths:
- Transparent and secure.
- Removes intermediaries.
- Programmable and flexible.
- Wide developer adoption.
Limitations:
- Gas fees: Transactions can be expensive when the network is congested.
- Complexity: Code vulnerabilities may lead to exploits.
- Scalability: The Ethereum blockchain still faces limitations on transaction speed, though upgrades like Ethereum 2.0 aim to solve this. As part of ongoing development, Ethereum transitioned from proof of work to proof of stake during ‘The Merge,’ significantly reducing energy usage and enabling the creation of new ETH through staking ether holdings. This transition improved network capacity and congestion management.
- Protocol upgrades and hard forks are part of Ethereum’s ongoing development to address security and scalability, with events like the emergence of Ethereum Classic resulting from such changes.
Ethereum Smart Contracts in Action
Some well-known use cases include:
- Uniswap: Automated market maker protocol for token swaps.
- MakerDAO: Stablecoin ecosystem with smart contracts enforcing collateral rules, where funds are managed and distributed automatically by smart contracts.
- Decentraland: Virtual land ownership powered by NFTs, with ownership transfers executed on the blockchain.
These examples demonstrate how Ethereum’s programmability changed the blockchain landscape forever. The Ethereum Foundation played a crucial role in supporting the development of the original blockchain, funding protocol upgrades, and responding to security incidents. The 2016 DAO hack led to a split, resulting in the creation of Ethereum Classic, which continues as the original, unaltered blockchain.
FAQs
What is a smart contract?
A smart contract is a coded agreement that runs on a blockchain. It executes automatically when predefined conditions are met, without intermediaries, and is recorded on a distributed ledger for transparency and security.
How does Ethereum work with smart contracts?
Ethereum hosts smart contracts through its decentralized network. Developers deploy code, and users interact with it. The consensus mechanism ensures that user transactions are validated and recorded securely on the blockchain, enforcing rules transparently.
What does Ethereum do beyond payments?
Ethereum powers decentralized applications, finance platforms, NFT markets, and even governance systems. It is widely used across industries like gaming, art, and digital identity. Ethereum’s native token, Ether, is recognized as a commodity rather than securities and is classified as a digital asset under various legal frameworks.
What is Ethereum used for most commonly?
Ethereum is most widely used for DeFi, NFTs, and Web3 applications. It is also the primary blockchain for experimenting with decentralized governance and finance.
Why are smart contracts important?
They allow automation, reduce reliance on intermediaries, and ensure transparency. They are the foundation for Web3 applications.
Conclusion
Ethereum smart contracts introduced the concept of programmable money, making it possible to design entire financial systems and applications on blockchain technology. While gas fees and scalability remain challenges, ongoing protocol upgrades continue to enhance the Ethereum blockchain network, improving its security, scalability, and overall functionality. The Ethereum ecosystem continues to expand, proving why it remains a leader in blockchain innovation.
As the crypto market evolves, understanding what a smart contract is and what Ethereum is used for will remain essential for both new and experienced traders.
Disclaimer: Trading digital assets involves risk and may result in the loss of capital. Always do your own research. Terms, conditions, and regional restrictions may apply.

Leave a Reply