
Ready To Place Your
Next Trade?
Choose a market, set your order, and manage risk in one place.

In crypto trading, risk never disappears. The market is fast, volatile, and influenced by both global finance and unpredictable sentiment, especially within crypto markets where these dynamics are most pronounced. By 2025, traders have more tools than ever to manage risk, but the question remains: should you hedge or should you short? The choice often depends on your individual risk tolerance and investment goals. Both strategies are designed to protect capital, but they operate differently and are suited to different market conditions, making it essential to select the right strategy for your specific situation.
This article explains how hedging compares to shorting, when to use each, and the rules that every trader should follow in bullish, bearish, and sideways markets. It also highlights how modern platforms like Bitunix provide tools and resources for traders to apply these strategies with confidence.
[ez-toc]

Both strategies are designed to protect capital, but they operate differently and are suited to different market conditions. The main difference is that hedging focuses on managing risk and protecting against potential losses by opening a position in the opposite direction of your current holdings, while shorting is primarily aimed at profiting from price declines.
Hedging is the act of opening a hedging position in the opposite direction to your existing holdings to reduce risk. For example, imagine you hold a long portfolio of Bitcoin and Ethereum. If you fear a downturn and want to mitigate potential losses, you might hedge by shorting a futures contract. If the market falls, your portfolio loses value but your hedge offsets some or all of those losses.
Shorting, on the other hand, is a directional bet. You are not only protecting existing positions, you are aiming to profit from falling prices. While hedging is defensive, shorting is offensive. The difference lies in the intent and outcome: hedging is about risk management and offsetting losses, while shorting seeks to generate profit from declines.
In practice, both tools overlap. Traders may hedge part of a portfolio with a small short, or they may go fully short to capitalize on bearish conditions. The key is knowing when each approach makes sense.
Hedging is best used when you already hold significant long exposure that you do not want to sell. This could be long-term Bitcoin spot holdings, altcoin spot holdings, or even DeFi spot holdings. Reasons to hedge include:
The purpose of hedging is not to maximize profit, but to stabilize investment performance.
Opening a short position through short selling is appropriate when you expect a clear downward trend and want to profit directly from potential profits as the price declines. However, these trading activities also expose you to potential losses if the market moves against your short position. Situations where such trades make sense include:
Shorting requires discipline because potential losses are theoretically unlimited. Unlike hedging, which limits volatility, improper shorting can lead to significant financial losses. Shorting aims to generate return in downturns but carries higher risk.

Even in bull markets, risk management is vital.
Many platforms offer features aimed at allowing traders to manage risk effectively in these scenarios.

Bear markets create both opportunity and risk.
Sideways or range-bound conditions demand patience, especially due to unpredictable price fluctuations.

These examples show that hedging and shorting are not mutually exclusive but context dependent.
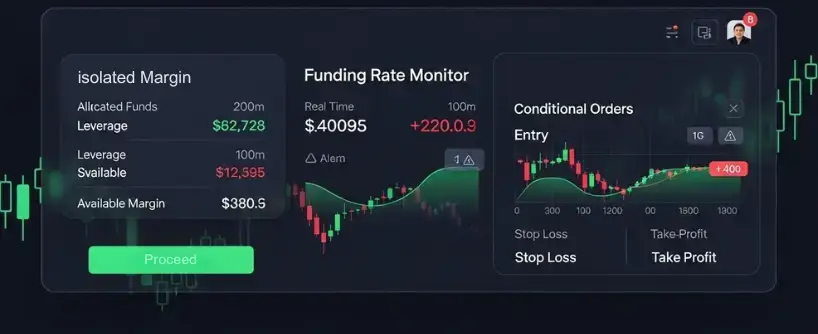
Bitunix provides tools that make both hedging and shorting more accessible and safer for traders. Our futures platform allows isolated margin accounts, meaning one trade cannot wipe out your entire balance. The platform also offers access to derivatives, such as futures and options, which are essential for risk management and hedging strategies in crypto trading. Funding rate monitors let you check whether holding a position will cost or pay funding fees. Conditional orders allow stop loss and take profit automation, removing emotional delays. Bitunix supports a wide range of trading activities, enabling users to implement various risk management techniques.
For those who want to strengthen their understanding, Bitunix Academy offers structured lessons on hedging strategies, shorting mechanics, and broader risk management. The Academy explains in detail how hedging works and how hedging works as risk management strategies, including real-world trading examples. Traders can search the web for Bitunix Academy to access tutorials, guides, and video content designed to explain strategies step by step.
Is hedging better than shorting?
Neither is universally better. Hedging reduces volatility, while shorting profits from declines. The right choice depends on your goals and market conditions.
Can I hedge without futures?
Yes. You can hedge by holding stablecoins, inverse ETFs, or options contracts. Options contracts give you the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a set price within a certain timeframe. This means you are not under the obligation to execute the trade, unlike other contracts that require you to fulfill the terms. Futures are simply the most direct method.
When is shorting too risky?
Shorting is too risky in strong bull markets or when funding rates make it too costly to hold.
Does Bitunix support hedging?
Yes. Traders can open opposite positions using futures, and Bitunix provides risk management tools like isolated margin and stop orders.
Should beginners hedge or short?
Beginners may find hedging safer, since it is defensive. Shorting requires experience and strict discipline.
By 2025, risk management in crypto requires more than intuition. Traders must choose whether to hedge or to short depending on the trend, their exposure, and their objectives. Hedging is defensive, limiting downside for existing holdings. Shorting is aggressive, seeking profit from price declines.
Both strategies demand discipline, proper stop placement, and awareness of funding costs. Platforms such as Bitunix give traders the tools to apply these methods while controlling risk, and Bitunix Academy provides education for those who want to learn in depth.
The most important rule is to know why you are entering a trade. Protecting capital is as important as seeking profit. Whether you hedge or short, preparation and discipline turn market volatility into manageable risk rather than uncontrollable losses.
Bitunix is one of the world’s fastest growing professional derivatives exchanges, trusted by over 3 million users across more than one hundred countries. Ranked among the top exchanges on major data aggregators, Bitunix processes billions in daily volume and offers a comprehensive suite of products including perpetual futures with high leverage, spot markets, and copy trading. Users can trade bitcoin and other major cryptocurrencies on the platform, taking advantage of advanced trading features. Known for its Ultra K line trading experience and responsive support, Bitunix provides a secure, transparent, and rewarding environment for both professional and everyday traders. Bitunix Academy adds structured lessons so you can build skills while you trade.
Bitunix Global Accounts
X | Telegram Announcements | Telegram Global | CoinMarketCap | Instagram | Facebook | LinkedIn | Reddit | Medium
Disclaimer: Trading digital assets involves risk and may result in the loss of capital. Always do your own research. Terms, conditions, and regional restrictions may apply.
