
The security and sustainability of blockchain networks depend on their consensus mechanisms. Bitcoin and Ethereum, the two largest cryptocurrencies, have taken different paths. Bitcoin remains committed to Proof of Work (PoW), while Ethereum transitioned to Proof of Stake (PoS) in 2022 with “The Merge.”
Understanding the differences between Proof of Work and Proof of Stake is crucial for traders and investors who rely on these networks. This article explains why Bitcoin chose Proof of Work, why Ethereum adopted Proof of Stake, and what this means for the future of crypto.
[ez-toc]
What is Proof of Work?

Proof of Work is the original blockchain consensus mechanism, first introduced by Bitcoin in 2009. In this model, miners compete to solve cryptographic puzzles. The first miner to solve the puzzle adds a block of transactions to the blockchain and earns a block reward in Bitcoin.
Key characteristics of Proof of Work:
- Energy-intensive: Requires specialized hardware and high electricity consumption.
- Security: Attacks require enormous computational power, making Bitcoin one of the most secure networks.
- Decentralization: Thousands of miners around the world participate in securing the network.
Bitcoin Proof of Work remains the gold standard for network security, but it has been criticized for its environmental footprint.
What is Proof of Stake?

Proof of Stake was developed as an alternative to Proof of Work. Instead of miners competing with computational power, validators are chosen to create new blocks based on the amount of cryptocurrency they “stake” as collateral.
Key characteristics of Proof of Stake:
- Energy-efficient: Validators do not require expensive mining rigs.
- Economic security: Validators risk losing their staked crypto if they behave dishonestly.
- Scalability: PoS networks can often process more transactions per second compared to PoW.
Ethereum’s transition to Proof of Stake drastically reduced its energy consumption and aligned the network with future scalability upgrades.
Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work: The Key Differences

| Feature | Proof of Work (PoW) | Proof of Stake (PoS) |
| Energy Use | High, requires mining hardware and electricity | Low, only requires validators to stake ETH |
| Security Model | Secured by computational power | Secured by economic incentives (slashing risk) |
| Participation | Miners with ASICs or GPUs | Anyone who stakes tokens |
| Scalability | Limited, slower block times | More scalable, supports future upgrades |
| Examples | Bitcoin, Litecoin, Dogecoin | Ethereum, Cardano, Solana, Polkadot |
Both systems provide strong security, but each comes with trade-offs in terms of energy, participation, and scalability.
Why Bitcoin Chose Proof of Work

Bitcoin’s creator, Satoshi Nakamoto, designed Proof of Work to solve the double-spending problem without requiring a central authority. Proof of Work is proven, simple, and battle-tested.
Reasons Bitcoin remains on Proof of Work:
- Unmatched security: The enormous computational power securing the Bitcoin blockchain makes it resistant to 51% attacks.
- Decentralization: Mining is distributed across the globe, preventing single points of failure.
- Immutable design: Bitcoin values stability and predictability, with minimal changes to its core protocol.
- Philosophy: Bitcoin is designed to be “digital gold,” prioritizing security over scalability.
For Bitcoin, Proof of Work is not just a technical choice. It is also an ideological one, aligned with Bitcoin’s role as a long-term store of value.
Why Ethereum Moved to Proof of Stake

Ethereum launched in 2015 with Proof of Work, but its roadmap always included a transition to Proof of Stake. This shift was completed in 2022 during The Merge.
Reasons Ethereum adopted Proof of Stake:
- Energy efficiency: Ethereum Proof of Stake uses over 99% less energy compared to Ethereum Proof of Work.
- Scalability: PoS enables future upgrades such as sharding, increasing Ethereum’s transaction throughput.
- Accessibility: Validators only need to stake ETH rather than invest in expensive mining hardware.
- Sustainability: Ethereum’s ecosystem of decentralized applications (DeFi, NFTs, gaming) benefits from environmentally friendly consensus.
By moving to Proof of Stake, Ethereum positioned itself as a versatile blockchain capable of scaling to global usage.
Ethereum Blockchain After the Merge
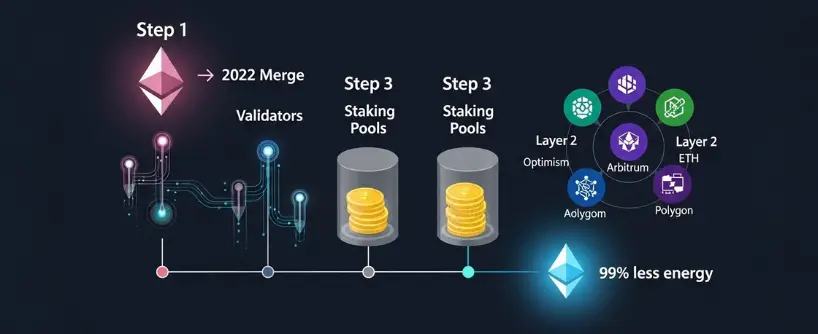
Post-Merge, the Ethereum blockchain operates under Proof of Stake with validators securing the network. Validators must stake at least 32 ETH to participate directly, although smaller holders can join through staking pools.
The impact of Ethereum Proof of Stake includes:
- Reduction in ETH issuance, making Ethereum potentially deflationary.
- Greater participation through staking pools and exchanges.
- A foundation for Layer 2 solutions and scalability upgrades.
Ethereum Proof of Stake continues to evolve, but the transition marked a defining moment in blockchain history.
Why Bitcoin and Ethereum Took Different Paths
The divergence between Bitcoin and Ethereum illustrates two different philosophies:
- Bitcoin prioritizes immutability, simplicity, and unmatched security through Proof of Work.
- Ethereum focuses on adaptability, scalability, and building an ecosystem of applications, making Proof of Stake more suitable.
Both approaches remain valid, serving different purposes within the crypto economy. Bitcoin continues as a store of value, while Ethereum powers programmable money, decentralized finance, and decentralized applications.
FAQs
What is Proof of Stake?
Proof of Stake is a consensus mechanism where validators stake cryptocurrency to secure the network. Validators are chosen to confirm transactions and create blocks based on their stake, consuming far less energy than Proof of Work.
What is Proof of Work?
Proof of Work requires miners to solve complex mathematical puzzles using computational power. This process secures the network and issues new coins as rewards for miners.
Why is Proof of Stake more energy-efficient?
Proof of Stake eliminates the need for high-powered mining equipment. Validators only need to run lightweight software and stake coins, reducing energy consumption by over 99%.
Why did Ethereum move to Proof of Stake?
Ethereum moved to Proof of Stake to improve scalability, reduce energy consumption, and prepare for future upgrades like sharding. The shift also opened opportunities for more users to participate in securing the network.
Why does Bitcoin still use Proof of Work?
Bitcoin remains on Proof of Work because it provides unmatched security and decentralization. The Bitcoin community values stability and the proven resilience of its existing system.
Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work: Which is better?
Neither is inherently better. Proof of Work prioritizes security and immutability, while Proof of Stake emphasizes scalability and sustainability. Their effectiveness depends on the goals of the blockchain network.
What is crypto staking?
Crypto staking is the process of locking up cryptocurrency in a Proof of Stake network to support operations such as transaction validation and block creation. Stakers earn rewards for their contribution.
How does Ethereum Proof of Work differ from Ethereum Proof of Stake?
Ethereum Proof of Work relied on miners to validate transactions, while Ethereum Proof of Stake relies on validators staking ETH. The shift reduced Ethereum’s energy usage and set the stage for greater scalability.
Conclusion
Bitcoin and Ethereum illustrate the diversity of blockchain innovation. Bitcoin chose Proof of Work for its unparalleled security and resilience, making it the foundation of decentralized digital money. Ethereum transitioned to Proof of Stake to scale its ecosystem of applications while addressing energy concerns.
For users and traders, understanding Proof of Stake vs Proof of Work is essential when evaluating networks for investment, staking, or development. Both mechanisms will continue to shape the future of blockchain, each serving a unique role in the global crypto economy.

