
The signing of the GENIUS Act into law by President Donald J. Trump signals the beginning of a transformative era for the cryptocurrency market in the United States. This landmark legislation is designed to establish the nation as a global leader in digital assets, setting a new standard for security and consumer protection in the rapidly evolving world of crypto assets and decentralized finance.
By creating a robust legal framework, the GENIUS Act aims to foster innovation while ensuring that consumers and investors can participate in the cryptocurrency market with greater confidence. As the law takes effect, it is expected to shape the future of stablecoins, digital assets, and the broader crypto ecosystem, positioning the U.S. at the forefront of the digital currency revolution.
[ez-toc]
Background: Why the GENIUS Act Was Created

In recent years, stablecoins like USDT and USDC have grown rapidly in use for remittances, trading, and yield-generating DeFi applications. However, regulators and lawmakers have raised concerns about systemic risk, lack of transparency, and consumer exposure to unbacked digital assets. The collapse of the algorithmic stablecoin TerraUSD (UST) in 2022, which erased over $40 billion in market value, added urgency to the legislative response.
The GENIUS Act was designed to address three primary concerns:
- Establishing clear oversight of fiat-backed and algorithmic stablecoins.
- Preventing systemic risk by imposing strict reserve and audit standards.
- Providing a federal framework to override inconsistent state-by-state crypto regulations.
According to official statements from the U.S. Treasury and congressional sponsors, the bill aims to create a “safe and innovation-friendly” environment for stablecoin usage while minimizing risks to the broader financial system.
What the GENIUS Act Covers
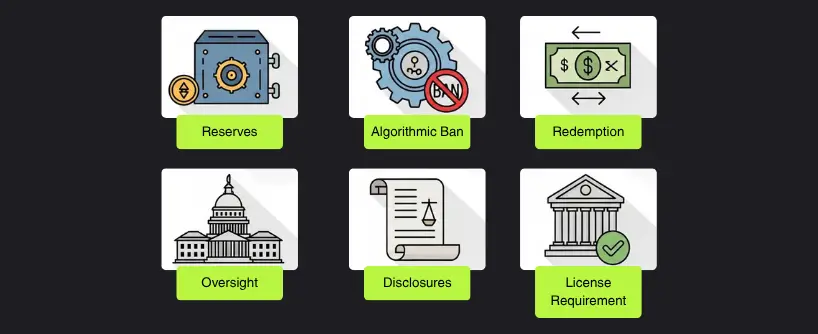
The GENIUS Act introduces a licensing regime for stablecoin issuers. It is now mandatory for any U.S. company issuing a stablecoin pegged to the U.S. dollar to register with either the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (OCC) or a newly designated federal crypto authority.
Key confirmed provisions include:
- 1:1 Backing Requirement: Every dollar-backed stablecoin must be backed by an equivalent amount of cash or highly liquid assets like Treasury bills. These reserves must be independently audited at least once per quarter.
- Prohibition of Algorithmic Stablecoins:The law temporarily bans the issuance of algorithmic stablecoins, defined as tokens that maintain their peg via complex code and arbitrage mechanisms rather than collateralized reserves. The ban is set to remain in effect for two years while a formal risk assessment is conducted.
- Redemption Rights: Issuers must guarantee that users can redeem stablecoins at par value on demand. This is aimed at reducing the risk of liquidity crises in the event of sudden redemptions.
- Federal Oversight: While states may continue to license and regulate certain digital asset entities, the GENIUS Act provides federal preemption for licensed stablecoin issuers. This ensures uniform national standards.
- Consumer Protection: Issuers must disclose their reserve composition, redemption process, risk exposure, and operational procedures in a public filing. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) is authorized to enforce deceptive practices.
- Limitations on Non-Bank Issuers: Only federally approved depository institutions or specially licensed entities can issue fiat-backed stablecoins. Tech companies and unregistered platforms are not permitted to issue their own coins without regulatory approval.
Immediate Impact on the Crypto Industry

The passing of the GENIUS Act represents the first time that stablecoins in the U.S. are subject to a uniform federal law. Crypto exchanges, wallet providers, and DeFi platforms will now need to verify that the stablecoins they support comply with the new framework.
1. For Stablecoin Issuers: USDC (Circle) and USDP (Paxos) are expected to remain compliant under the act. Tether (USDT), however, may face increased scrutiny if its reserve disclosures are not aligned with U.S. audit standards. Companies will have to apply for a federal license, maintain ongoing disclosures, and comply with redemption protocols.
2. For Exchanges and Wallet Providers: Platforms that offer stablecoins to U.S. users must ensure that they are listing only federally compliant stablecoins. Any platform supporting non-compliant or algorithmic stablecoins risks enforcement action or delisting.
3. For DeFi and dApps: Decentralized platforms integrating stablecoins into lending or liquidity protocols must now build in mechanisms to ensure only whitelisted, compliant tokens are used. This could impact DeFi TVL (Total Value Locked) in the U.S.
Smart Contract Regulations: Coding Compliance into Crypto

Recognizing the pivotal role of smart contracts in decentralized finance, the GENIUS Act sets forth clear guidelines for their use and regulation. Smart contracts—self-executing agreements coded directly onto blockchain networks—are essential for automating transactions and enabling complex financial interactions without intermediaries. The legislation requires that all smart contracts used in connection with regulated stablecoins comply with established AML and KYC standards, ensuring that these digital agreements uphold the same level of security and transparency as traditional financial contracts. By embedding compliance into the very code of smart contracts, the Act supports the continued growth of decentralized finance while safeguarding users and the integrity of the broader cryptocurrency market.
Institutional Reactions

Large financial institutions have responded positively to the GENIUS Act. BlackRock, JPMorgan, and Fidelity issued separate statements noting that regulatory clarity in the stablecoin space could enable more traditional finance players to enter the digital asset space.
Fintech firms like PayPal and Stripe, which are exploring stablecoin integration for payments, also welcomed the legislation, stating it gives them a legal basis to innovate with programmable dollars.
However, several blockchain advocacy groups expressed concerns that the prohibition of algorithmic models may stifle innovation. They argue that future-proofing legislation must allow for experimentation within a controlled environment.
Global Implications
The GENIUS Act may serve as a model for other jurisdictions. Countries in the EU, Latin America, and parts of Asia have followed U.S. regulatory developments closely, particularly as many dollar-backed stablecoins are used internationally.
If other nations adopt similar frameworks, the GENIUS Act could accelerate the global legitimization of stablecoins as compliant financial instruments, potentially opening up broader use cases in payments, trade settlement, and tokenized assets. Additionally, the GENIUS Act’s approach may influence future legislative developments and global regulatory trends as countries seek to harmonize their digital asset policies.
Conclusion
The GENIUS Act officially introduces the first full-spectrum regulatory structure for stablecoins in the United States. By addressing critical gaps in reserve backing, redemption rights, and issuer accountability, the law is expected to bring greater trust and institutional participation in the crypto economy.
The stablecoin landscape in the U.S. is now entering a new era. For investors, platforms, and developers, this legislation creates both compliance requirements and new growth opportunities.

