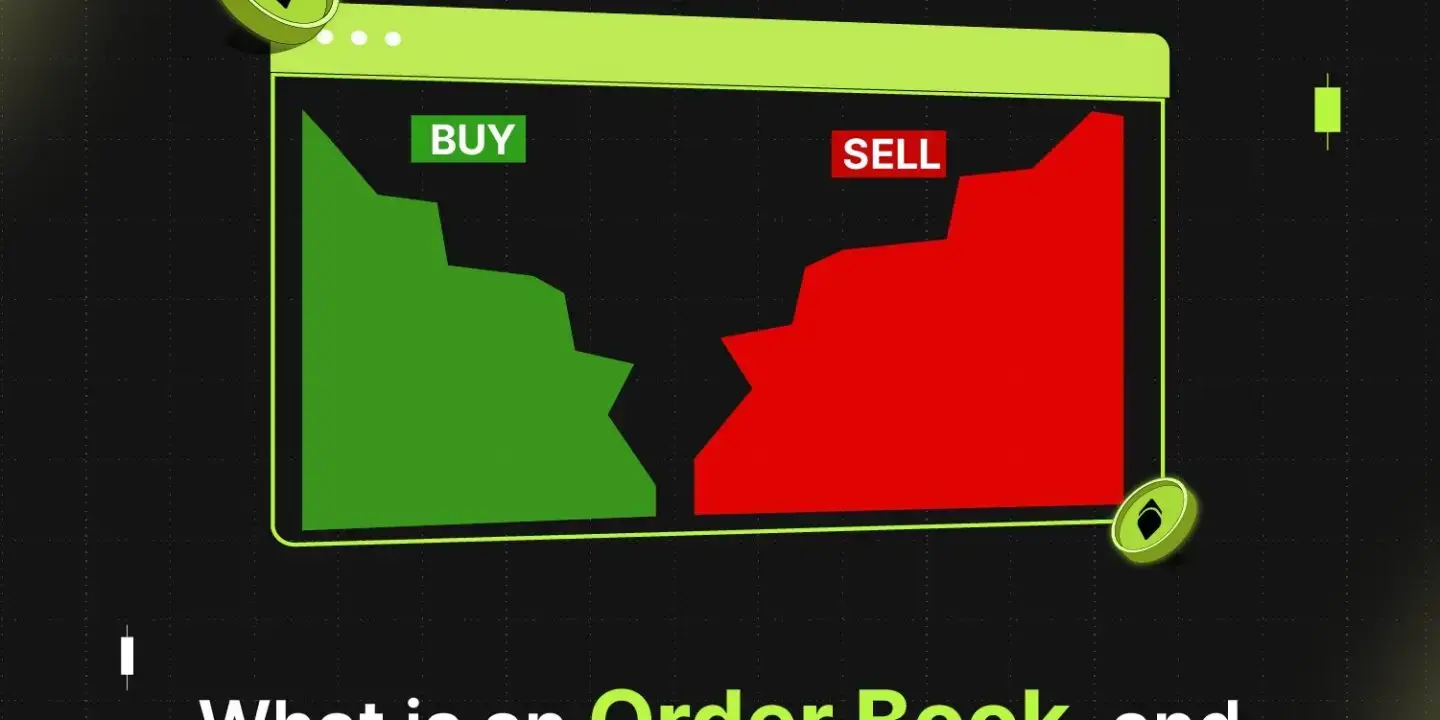
An order book in crypto is a real-time electronic list of all open buy and sell orders for a specific trading pair on an exchange. It shows the bid (buy) and ask (sell) prices, along with the quantities traders are willing to buy or sell. This gives a transparent view of order book depth, liquidity, and market sentiment.
For example, looking at a BTC order book shows all the buy and sell interest for Bitcoin at different price levels. Traders rely on this information to gauge supply and demand, place efficient orders, and anticipate potential price movements.
What are the key components of an order book?
Understanding the basic structure of an order book is essential for interpreting the data it provides. Typically, an order book consists of the following elements:
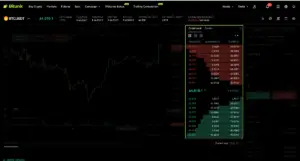
- Bids (Buy Orders): Represent the demand for the asset, showing the prices and quantities that traders are willing to pay. Bids are listed from highest to lowest price, indicating what buyers are prepared to spend.
- Asks (Sell Orders): Represent the supply of the asset, displaying the prices and quantities traders are willing to sell at. Asks are listed from lowest to highest price, indicating what sellers are willing to accept.
- Sum: This shows the cumulative quantity of the asset that would be filled if a buy or sell order is placed up to that price level. It provides a way to see the depth of the order book at each price level.
- Quantity: This is the number of BTC available to buy or sell at each price level. Higher quantities at a particular price level indicate significant interest or potential price support (for buy orders) or resistance (for sell orders).
- Order Size: Denotes the quantity of the asset that traders wish to buy or sell at a specific price point.
- Price Levels: Organizes the order book by these levels, helping traders visualize market depth and potential price movement.
- Market Depth: Shows the volume of buy and sell orders at each price level. Higher market depth means greater liquidity, which facilitates large trades without significant price changes.
- Spread: The difference between the highest bid and the lowest ask price. A narrower spread indicates a more liquid market, while a wider spread suggests lower liquidity and higher volatility.
Order Book Depth – Why It Matters
Order book depth refers to how many buy and sell orders exist at different price levels. A deep book with many bids and asks means strong liquidity, making it easier to execute large trades without moving the price significantly.
A shallow book has fewer orders, so even small trades may cause big price swings. For example, in a thinly traded altcoin, a market order of just $5,000 could move the price several percentage points. In contrast, a deep Bitcoin order book can absorb millions in trades with minimal price impact.
How Does an Order Book Work?
An order book constantly updates as new buy and sell orders are placed or canceled. Three key order types influence it:
- Market Orders: Filled immediately at the best available price. They reduce liquidity in the book.
- Limit Orders: Placed at a specific price and sit in the order book until matched or canceled. They add liquidity.
- Stop Orders: Trigger once a set stop price is reached, becoming a market or limit order.
Example: If a trader places a market buy order for 10 BTC, it will be matched against the lowest available sell orders. If the sell side is shallow, the buy may push the price upward by consuming multiple levels.
How to Read a Crypto Order Book
Learning how to read order book crypto displays is like reading supply and demand in real time.
Step-by-Step:
- Check Bid and Ask Sides:
- Highest bid = max price buyers will pay.
- Lowest ask = min price sellers will accept.
- Note the Spread:
- Narrow spread = liquid market.
- Wide spread = volatile or illiquid.
- Analyze Market Depth:
- Look at cumulative quantities (sum column) to gauge buying or selling power.
- Spot Buy and Sell Walls:
- Large clusters of orders at one price form “walls” that act as support (buy wall) or resistance (sell wall).
- Monitor Order Flow:
- Watch how quickly orders are filled or canceled. Rapid buying often signals bullish sentiment, while heavy sell pressure can signal bearish conditions.
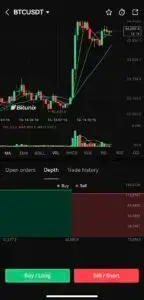
How to Check Order Book of Crypto
Wondering how to check order book data in practice?
- Almost every exchange, including Bitunix, Binance, and KuCoin, provides an Order Book tab for each trading pair.
- Data aggregators like CoinGlass also show global order book depth for major assets such as BTC or ETH.
- To check your own executed trades, use the trade history section in your account, not the public order book.
So if you want to see a BTC order book, simply open the BTC/USDT pair on your chosen platform and navigate to the order book view.
Examples of Order Book in Action
Imagine the BTC/USDT order book:
| Bids (Buy Orders) | Asks (Sell Orders) |
| 10 BTC @ $60,000 | 8 BTC @ $60,100 |
| 12 BTC @ $59,950 | 7 BTC @ $60,150 |
| 15 BTC @ $59,900 | 10 BTC @ $60,200 |
- Here, the highest bid is $60,000 and the lowest ask is $60,100, making the spread $100.
- A large buy wall at $59,900 (15 BTC) may act as support, while a sell wall at $60,200 (10 BTC) may act as resistance.
This is how traders anticipate short-term moves.
Why Study Order Books in Crypto Trading?
Studying order book crypto data is critical for:
- Finding support and resistance: Buy/sell walls can act as barriers.
- Spotting imbalances: More bids than asks may signal upward momentum.
- Placing efficient limit orders: Reduces slippage by targeting high-liquidity levels.
- Avoiding manipulation: Sudden fake walls (spoofing) can mislead traders.
In short, the order book is a powerful tool, but it should be combined with technical indicators (RSI, moving averages) and fundamental analysis for a complete trading strategy.
How Do I Track My Crypto Transactions?
The order book shows open interest and liquidity, not personal trades. To track your own orders or completed trades:
- Check your exchange account history.
- Use blockchain explorers for public transaction verification.
- On Bitunix, your trade history is visible directly in the trading dashboard.
Conclusion
An order book crypto display provides unmatched transparency into supply and demand. By learning how to read an order book, analyzing order book depth, and spotting imbalances, you can better anticipate price movements.
For beginners, the process starts with checking the spread, identifying buy/sell walls, and combining order book insights with technical tools. For professionals, it becomes a key part of advanced risk management.
Mastering order book analysis will make you more confident, whether you are studying the BTC order book or exploring smaller altcoin markets.
FAQs
What is an order book in crypto?
An order book in crypto is a real-time list of buy and sell orders for a trading pair, showing bids, asks, order sizes, and market depth.
How to read the order book in crypto?
To read order book crypto, check the bid side (buyers), ask side (sellers), and the spread. Large buy walls suggest support, while large sell walls suggest resistance.
How to check order book of crypto?
You can check any order book crypto by opening the trading pair on exchanges like Bitunix or Binance and clicking the “Order Book” tab.
Where can I find a crypto order book?
Every exchange provides an order book. For broader data, use aggregators like CoinGlass or CryptoQuant to see combined liquidity across platforms.
How do I track my crypto transactions?
Use your exchange account’s trade history or blockchain explorers. Order books only show pending and open orders, not your personal completed trades.
How to study order books in crypto?
Watch market depth, bid-ask spread, and order flow. Combine with chart analysis for better entries and exits.
How to understand order book in crypto?
Think of it as a snapshot of supply and demand. Bids show demand, asks show supply, and the spread plus order walls show where the market might move.
How to see order books in crypto?
Go to the trading interface of your exchange. For example, open BTC/USDT on Bitunix and select the “Order Book” view.
What is the best way to study crypto?
Combine order book analysis with indicators (EMA, RSI) and news tracking. Studying order flow alongside charts provides the best insights.
What is BTC order book?
The BTC order book is the real-time list of Bitcoin buy and sell orders on an exchange. It helps traders see liquidity, spreads, and potential short-term moves.
About Bitunix
Bitunix is one of the world’s fastest growing professional derivatives exchanges, trusted by over 3 million users across more than one hundred countries. Ranked among the top exchanges on major data aggregators, Bitunix processes billions in daily volume and offers a comprehensive suite of products including perpetual futures with high leverage, spot markets, and copy trading. Users can trade bitcoin and other major cryptocurrencies on the platform, taking advantage of advanced trading features. Known for its Ultra K line trading experience and responsive support, Bitunix provides a secure, transparent, and rewarding environment for both professional and everyday traders. Bitunix Academy adds structured lessons so you can build skills while you trade.
Bitunix Global Accounts
X | Telegram Announcements | Telegram Global | CoinMarketCap | Instagram | Facebook | LinkedIn | Reddit | Medium
Disclaimer: Trading digital assets involves risk and may result in the loss of capital. Always do your own research. Terms, conditions, and regional restrictions may apply.

